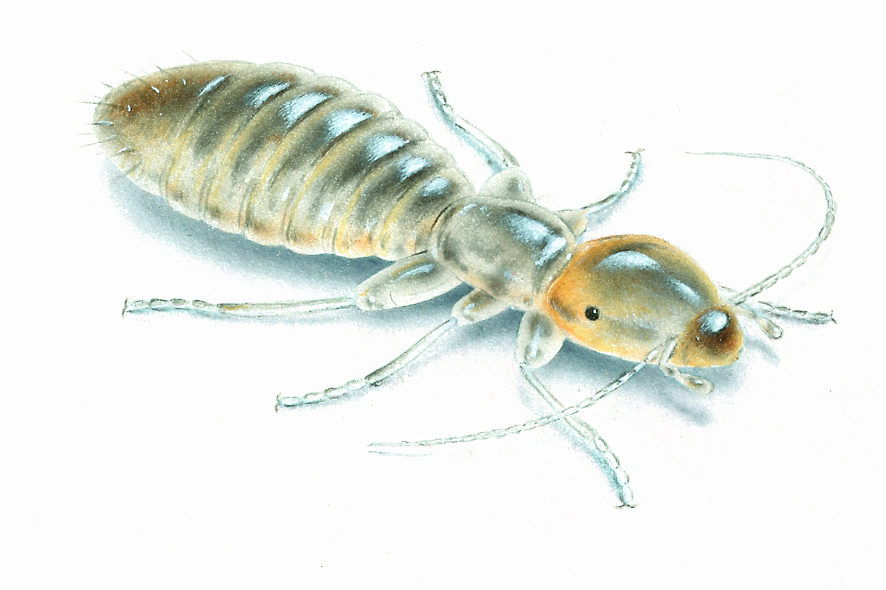
Body lice (Pediculus Humanus Humanus or Pediculus Humanus Corporis) are bloodsucking parasites that feed exclusively on human blood. Body Lice live and nest in human clothing and move to the skin in order to feed. Body lice cause intense itching and are dangerous transmitters of disease. Whereas head and pubic lice do not spread diseases to humans, body lice can transmit Typhus, Trench Fever, and Relapsing Fever. Any active body lice infestations must be treated as promptly as is possible. A lice infestation is known as ‘Pediculosis.’
In appearance, a body louse is nearly identical to a head louse. Body lice are between one to three millimeters long (roughly the size of a sesame seed) and light gray in color. After feeding, they become darker and can take on a reddish tint. Females are larger than males. The insects are flat and are made up of three fused but visibly separate parts, a head, thorax, and abdomen. After feeding, they excrete a small dark red dirt-like spot known as frass.
Body lice live and lay eggs in the seams and folds of clothing or bedding and generally only move to the skin in order to feed. They feed close to the clothing they inhabit and, as such, itching and bites are generally experience where clothing is tighter or closer to the skin such as waistlines, around bra straps, and so forth. Body lice must be around the heat of the human body in order to survive. After being removed from the presence of a human host, a body louse will die in a matter of days.
Infestations of body lice are easily treated and avoidable through basic hygiene and, for this reason, are relatively rare in developed countries. Infestations are most often seen in populations without access to regular bathing or changes in clothing such as homeless people and refugees. Body lice are contagious and are passed from person to person by direct contact or by sharing of clothing or bedding with an infested person. Body lice feed only on humans and, as such, cannot be transmitted by animals.
Body Lice Treatment
Body Lice treatment is extremely simple given the right conditions. Infestation is fully and easily treatable by maintaining relatively minimalistic standards of hygiene. If you have identified an infestation, destroy or carefully wash all clothing and bedding you have used in the past week. Items that are not discarded should be washed and dried on the hottest possible cycles (at least 130° Fahrenheit). Body Lice in infested clothing that is removed and not worn for at least a week will die as well.
A doctor may prescribe a pediculicide (lice insecticide) in the form of a cream to wash the body with, however, this is most likely not necessary. Bathing daily and changing and laundering clothes on at least a weekly basis is enough to clear infestations completely.
