 Pthirus Pubis is a type of louse more commonly known as pubic lice, crab lice, or colloquially, crabs, which inhabits pubic hair though it can also live on eyelashes. Like all other lice that affect humans, pubic lice live on and between hairs on their hosts and feed by sucking blood. Crab lice are spread almost exclusively through intimate sexual contact though it is possible to contract an infestation through shared use of towels, bedding, or clothing.
Pthirus Pubis is a type of louse more commonly known as pubic lice, crab lice, or colloquially, crabs, which inhabits pubic hair though it can also live on eyelashes. Like all other lice that affect humans, pubic lice live on and between hairs on their hosts and feed by sucking blood. Crab lice are spread almost exclusively through intimate sexual contact though it is possible to contract an infestation through shared use of towels, bedding, or clothing.
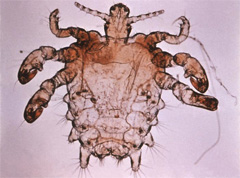
Pthirus Pubis are known as crab lice because their appearance is similar to that of a very small crab. Crab lice are between one to two millimeters long, flat, and have six legs. The lice’s back legs are clawed and longer than their other legs and the lice are nearly round in shape. Pubic lice live and lay their eggs (nits) on the relatively tough and coarse hairs found in the pubic region. They are also able to live in areas with similar hairs such as in moustaches, beards, armpits, or eyelashes, but this is significantly less common.
Having pubic lice is a disease that is known as Pediculosis pubis or ‘crabs.’ The primary symptom of crabs is severe itching, which is caused by hypersensitivity of the body to the crab louse’s saliva. The skin around bites may or may not become gray-blue, but this passes within a few days of treatment. Repeated scratching can cause open sores. Though crab lice are small, they and their eggs may be visible to the naked eye.
Pubic Lice Treatment
Getting rid of pubic lice is a simple process. The first step is diagnosis. Hair should be combed through with a nit comb to look for nits and live lice. If live lice are found they can be removed with tweezers and examined under a magnifying glass. Once a live infestation is identified, every other member in the household needs to be examined for an infestation. In addition, as crabs is a sexually transmitted disease, every person with whom the infested person has had sexual contact with over the past month should be notified and examined as well.
Getting rid of crabs is much the same process as getting rid of head lice. You will need to purchase a specialized pediculicide (lice insecticide) and a nit comb at your local pharmacy. Follow the instructions on the package carefully. Wash the area with water but without shampoo or conditioner. Using shampoo or conditioner will make it harder for the medicine to stick and thus less effective. Apply the treatment and rinse according to instructions. Do not wash the area with shampoo or conditioner for at least two days as it may wash out the medicine. Retreatment is not always needed but is recommended after three to seven days to prevent reinfestation. After treating, comb through the hair with a nit comb once a day and remove live and dead lice and nits. Do not use home remedies concurrently as they may wash out the treatment rendering it less effective.
Most over-the-counter creams for pubic lice use permethrin as the active ingredient. If after treatment you are seeing no improvement, you may have drug-resistant lice. See a doctor and ask for a prescription medication. Prescription medications are not necessarily more powerful but use different ingredients which the lice may not be resistant to. During the treatment you must avoid sexual contact. In addition, do not share towels, clothing or bedding with other people. Wash and dry clothing you have worn and items you have come in contact with in a machine on the hottest setting.
